Introduction
Subsistence farming with bullocks has mostly been replaced by enormous areas of land ploughed by tractors and mechanized harvesters, as well as the use of GMOs to boost crop immunity. And the next step in agriculture’s evolution is a large-scale single crop unit that would provide exceptional output since drones would be used for numerous activities.
Food security will be an important concern with a rapidly rising population, environmental degradation, global warming, and a decline in arable land, and feeding the teeming population would necessitate agricultural innovation and substantial use of drone technology. By 2050, the global population will be over 10 billion, and agricultural productivity would need to be doubled to avoid food shortages.
What is Food Security?
According to the 1996 World Food Summit, food security is defined as having physical and economic access to adequate safe and nutritious food that fits their dietary needs and food choices for an active and healthy life at all times.
Food security is defined at the 1996 World Food Summit. The four major dimensions of food security are:
- Physical availability of food: Food availability addresses the “supply side” of food security and is determined by food production, stock levels, and net trade.
- Economic and physical access to food: An adequate supply of food at the national or international level does not guarantee household food security. Concerns about limited food access have led in a stronger governmental emphasis on income, expenditure, markets, and prices in achieving food security goals.
- Food utilization: Utilization is typically considered as the process through which the body extracts the most nutrients from diet. Individuals’ adequate energy and nutritional intake is the outcome of proper care and feeding practices, food preparation, diet diversification, and intra-household food distribution. When combined with good biological utilization of food consumed, this determines an individual’s nutritional state.
- Stability of the other three dimensions over time: Even if your food intake is acceptable today, you are deemed food insecure if you have insufficient access to food on a regular basis, putting your nutritional status at danger. Adverse weather, political unrest, or economic reasons (unemployment, increased food prices) can all have an impact on your food security.
The Use of Drone in Food Security
Capture Vast Volumes of Data Instantly
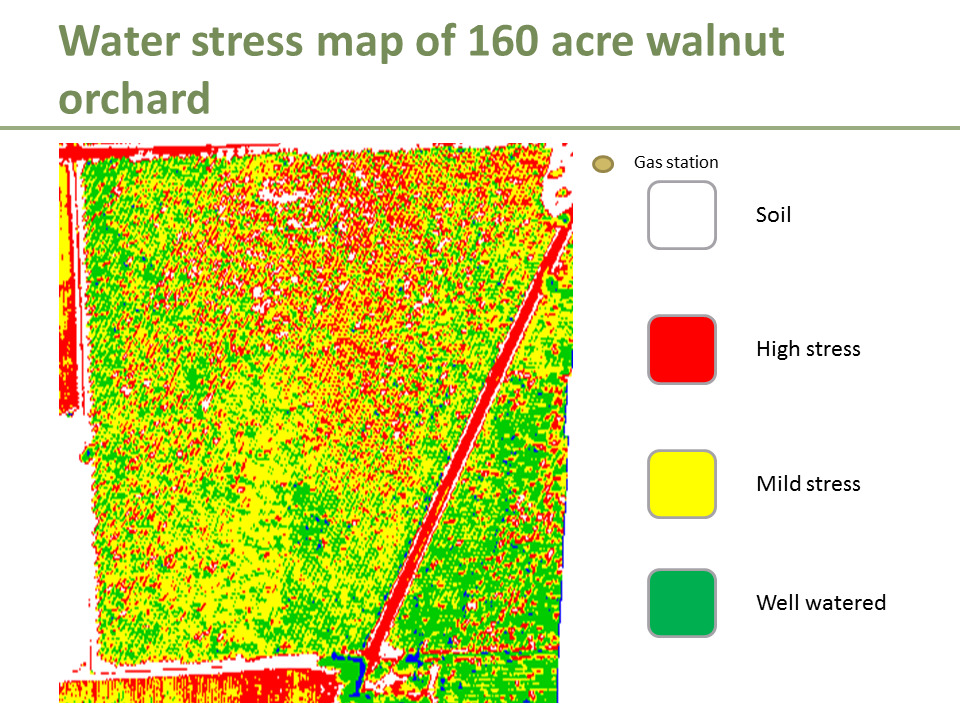
Drones in agriculture acquire massive amounts of data quickly and accurately. This data is used to increase agricultural output while conserving resources such as water and fertilisers. Drones equipped with cameras capture high-resolution images of crops, which can then be examined to detect stress, disease, or pests. This information is useful for making appropriate crop management decisions, such as when to apply fertilizer or how regularly to control pests.
Save Time & Money
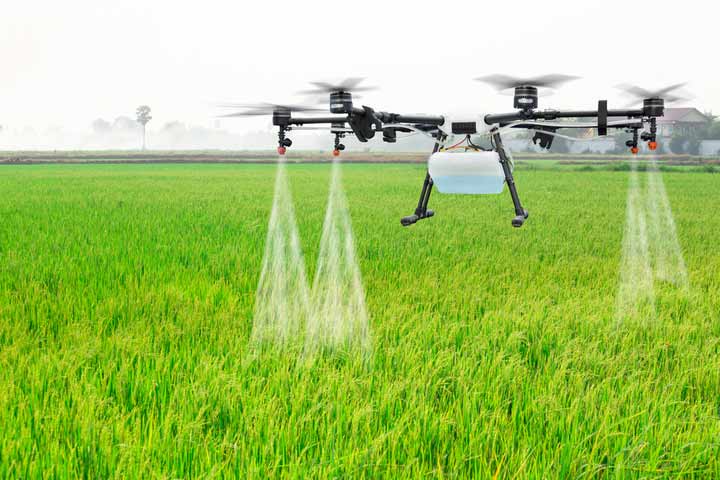
Farming tasks could be carried out more efficiently. Drones, for example, can be used to spray pesticides on crops, saving time and money over traditional techniques. They can also be used to plant seeds and conduct other chores that would normally be done by hand, reducing labor costs and increasing farm efficiency.
Precision Farming
Precision agriculture, which employs GPS, GNSS, and drones, maximizes agricultural productivity and assists farmers in determining which crop is most suited to the soil quality and geological circumstances. The use of technology also alerts farmers in advance to take preventative measures in the event of unforeseeable natural calamities. While precision agriculture is not a new concept, it is experiencing changes and using new technologies to improve agricultural problem optimization. Drones play an important part in precision agriculture, and their use will only grow in the future to give the best quality results.
Determine the Exact Quantity of Fertilizers
Other types of drones can help determine the precise amount of fertilizer required in the fields. This will not only save fertilizers but also maintain ecological balance by emitting fewer ozone-depleting gases with tailored fertilizer use.
Conclusion
Finally, drones have the potential to improve food security by increasing agricultural yields, reducing resource consumption, and carrying out tasks quickly and effectively. Many businesses and institutions are already using drones in agriculture, and governments and international organisations are looking into how drones might help disadvantaged countries improve their food security. While there are some challenges to overcome, such as legislation and expense, the usage of drones in agriculture is expected to increase in the future.
References
Drones to boost agricultural production and help maintain food security
From Field to Table: How Drones are Modernizing Agriculture and Ensuring Food Security




