What is Environmental Conservation?
Environmental conservation involves safeguarding the natural world from collapsing due to human activities that disrupt its equilibrium, such as unsustainable farming, deforestation, and the combustion of fossil fuels. These practices result in detrimental consequences such as polluted air, plastic contamination, the obliteration of natural habitats, and most urgently, the onset of climate change. Experts caution that without timely intervention, this trajectory will lead to a heightened occurrence of natural catastrophes, escalating sea levels, and intensified extreme weather events. This, in turn, will trigger the collapse of ecosystems, the widespread extinction of species, shortages of food, and the displacement of populations worldwide.
Environmental conservation and preservation, while often used interchangeably, exhibit expressed distinctions. Conservation pertains to the responsible oversight of the environment and its resources, catering to both current and future requirements. Conversely, preservation adopts a closer approach, safeguarding the environment, lands, and natural resources from human consumption, and maintaining them in their original state. If these lands are to be utilized by humans, they should be solely for the purpose of appreciating and drawing inspiration from their natural beauty.
Environmental Friendly Drones
Drones are finding expanding roles in various aspects of life due to their versatile range of potential uses. They are already being utilized in fields such as science, renewable energy, geology, and agriculture, ushering in a future full of possibilities. However, their contribution to sustainability raises the question of whether they are a supportive force or a detrimental factor.
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, commonly referred to as drones, are essentially flying automatons that can be steered from a distance or navigate autonomously using pre-programmed flight paths governed by software, onboard sensors, and a global positioning system (GPS). The proliferation of drone usage has been driven by their ability to remain airborne for prolonged periods compared to piloted aircraft, their cost-effectiveness relative to other aerial vehicles, and their remote operation which eliminates risks to flight crews.
Drones for Forest Conservation
We recognize that plants and trees play essential roles as sources of air, nourishment, and contribute to various everyday items, including the paper you use for writing. Any disruption in this intricate balance can lead to disturbances in both the water cycle and the food chain. Afforestation involves the replanting of trees that have been removed, serving to uphold a stable ecosystem. The effort to increase tree planting and prevent the removal of existing ones is crucial due to the substantial role that trees play in maintaining ecological equilibrium.
Utilizing Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) sensors, cameras, microphones, and satellite systems, along with control and robotics, precision agriculture methods facilitate the automated, real-time surveillance of plant health, productivity, and ecological effects, thereby enhancing operational effectiveness. Wider integration of these innovations has the potential to curtail emissions by approximately 4.3%, all the while mitigating product losses stemming from diseases.
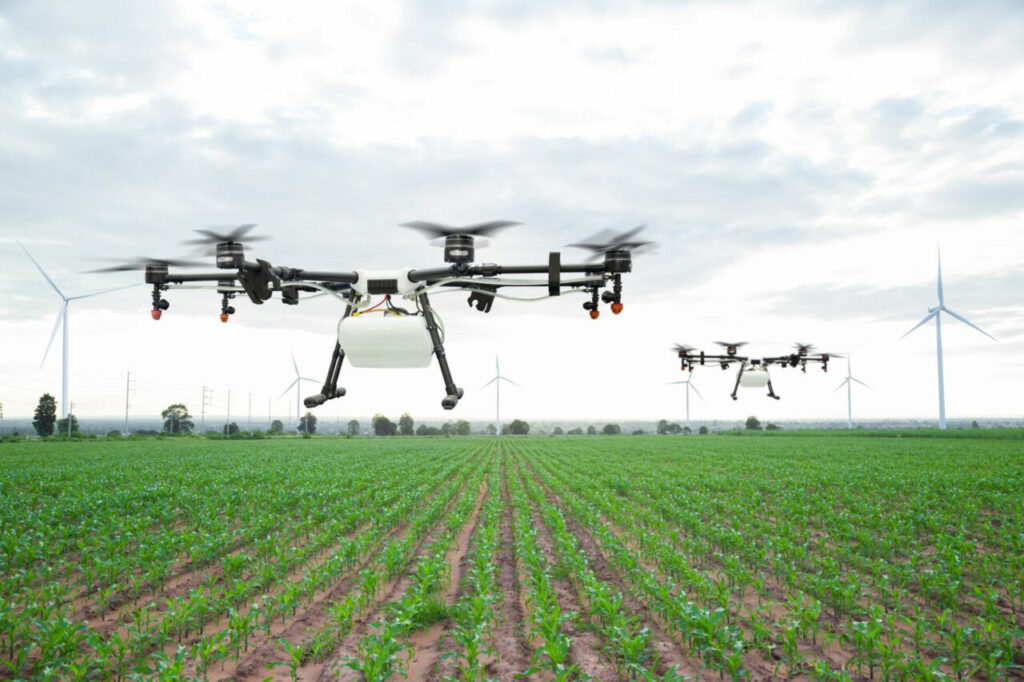

In the field of forestry, drones have versatile applications including defining and mapping tree stands, devising strategies for harvesting, estimating forest composition and inventory, gauging carbon levels, evaluating damages, detecting forest diseases and pests, creating stand maps, identifying forest fires and mapping their aftermath. Furthermore, drones find utility in tasks like ecological mapping, overseeing park ecosystems, promoting tourism, generating topographic models, mapping soil erosion, monitoring wildlife, and identifying encroachments and trespassing incidents.

Drones for lowering Air Emmisions.
The surging desire for swift and touchless deliveries has impelled companies to explore automated parcel delivery vehicles capable of circumventing urban congestion to swiftly reach customers. The extensive incorporation of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) to supplant a portion of initial and concluding leg truck pickups and deliveries could revolutionize the energy landscape of transportation, reshaping consumption patterns and transitioning fuel utilization from fossil fuels to electricity. It is imperative to optimize both delivery drones and their systems to achieve maximal energy efficiency. In this context, it is important to get insights from stakeholders and researchers by elucidating the energy consumption of package-delivery drones.
A comparison conducted on the environmental implications of diverse ‘last-mile’ delivery methods, responsible for transporting packages during their final phase, reveals a remarkable contrast: drone deliveries exhibit 84% fewer greenhouse gas emissions per parcel compared to diesel trucks, accompanied by a substantial reduction of up to 94% in energy consumption per parcel. The deployment of drones to facilitate the ultimate leg of small item distribution presents a highly promising avenue for curbing carbon dioxide emissions stemming from vehicle travel between distribution points and individual residences.

Drones for Waste Management
Particularly in developing nations and densely populated regions, a significant quantity of waste is thoughtlessly discarded on streets and roads on a daily basis. Waste takes on diverse forms, each with its own impact on both people and the environment. Non-biodegradable waste becomes part of the food chain, potentially resulting in sickness, illness, or even death. In contrast, organic waste is linked to diseases, outbreaks of pests, and the pollution of water and soil. Toxic waste, as the name suggests, is extremely harmful and is often generated by industrial and chemical sectors. This type of waste not only renders the land uninhabitable but also taints it with toxicity for an extended duration.
Among the notable contributions drones make to assist waste management, data gathering stands out prominently. Drones can reach locations inaccessible to humans, leading to reduced research costs and enhanced precision in data collection.
Researchers have harnessed drones to evaluate surface reflectance, capturing data on the extent of solar energy reflected and absorbed by specific regions. This information allows garbage management companies can go one step further with drone technology by monitoring and controlling the water quality and garbage with drones fitted with certain cameras. Since water is used extensively in many industrial processes, which results in significant wastewater production, businesses can enhance and use the most effective wastewater treatment techniques.

Drones for Ocean Conservation
To study and observe oceans and the deep-sea ecosystems impacted by excessive fishing, drones are employed. Governments striving to rehabilitate fish populations in these areas establish conservation zones and sanctuaries that prohibit human fishing. Yet, adherence to sanctuary regulations by all fishing enterprises is not guaranteed.
Governments and scientists need to oversee and enforce regulations aimed at safeguarding marine habitats. Employing drones for surveillance within these protected zones offers a cost-effective substitute for using coast guard helicopters and boats.

Drones are being employed by ocean ecologists and conservationists to offer aerial perspectives on the state of ocean health.
Oceanic ecosystems serve as the lifeblood of the planet, and their well-being is vital for the overall health of interconnected ecosystems worldwide. Unfortunately, numerous ocean ecosystems are undergoing rapid deterioration, necessitating monitoring efforts to garner insights for preventing further decline.
However, monitoring many of these ecosystems can pose challenges. Some are situated too far offshore or in areas with water too shallow for conventional boats to access. In certain cases, data collection relies on aerial surveys, but this method has limitations and contributes to a significant carbon dioxide footprint. While other, more cost-effective alternatives are available, they often involve invasive techniques that can disrupt or distress wildlife.
5 Major Importance of Environment Conservation
To Avoid Exploitation of Natural Resources
According to data from Worldometer, the global human population currently stands at 7.9 billion and is projected to reach 10 billion by the year 2057. As the human population continues to rise, there is a corresponding surge in resource consumption. Essential natural resources such as water, air, sunlight, arable land, metal ores, and fossil fuels are pivotal for sustaining our way of life and ensuring comfort.
Given our heavy reliance on fossil fuels for energy needs, the potential scarcity of these resources could introduce unforeseen challenges on a global scale, particularly considering the fact that their formation spans millions of years. Moreover, our freshwater resources account for just 3% of the Earth’s total water bodies, with a mere 1% available for vital functions like power generation, irrigation, and everyday use. The current utilization patterns of these resources could eventually culminate in a crisis for future generations.
Beyond mineral and water resources, escalated deforestation and other human-driven activities have led to the depletion of natural forests and their ecosystems. This, in turn, precipitates a host of other environmental problems. Therefore, grasping the imperative of environmental conservation is not only crucial for the well-being of forthcoming generations but also for the coexisting species that inhabit our shared planet.

To Keep Balance in Our Ecosystem
The primary focus lies in upholding the natural equilibrium within an ecosystem. Just as we take resources from the environment, it’s imperative that we give back to maintain this equilibrium. Various factors can disrupt this balance, including the introduction of new species, sudden species mortality, natural disasters, or human-induced factors. Our forests play a crucial role in providing drinking water to many of the world’s renowned cities, contributing about one-third of this supply. Additionally, these forests serve as a shared habitat for numerous species, including 80% of amphibians, 75% of birds, and 68% of mammal species.
The expansion of paved surfaces in urban areas not only reduces the release of water vapor through vegetation but also adds to groundwater pollution if road salt, used for melting ice, enters the natural drainage system. The augmentation of street trees could have positive impacts, potentially cooling the air temperature in summer by 0.5 to 2.0 degrees Celsius, benefiting approximately 68 million individuals. Ecosystem degradation has already affected around 40% of the global population, and this trend can be averted through the active practice of environmental conservation.

To Prevent Human-Caused Natural Disasters
Apart from the annually occurring human-made accidents, certain natural catastrophes are significantly influenced by escalated human activities. A notable instance is the Chornobyl disaster of 1986, situated in northern Ukraine, then part of the Soviet Union. The release of radioactive toxins in that region rendered the land uninhabitable due to radioactive contamination. If humans cannot reside there, it raises doubts about the viability for other organisms.
Further examples of such natural calamities encompass floods, which led to the loss of approximately 6.8 million lives in the 20th century. Astonishingly, these too have roots in human activities. Factors like deforestation, climate alteration, prolonged periods of rainfall, and the rise in sea levels contribute to the heightened impact of floods. It’s not just floods; other forms of natural disasters are equally influenced by human actions. This underscores the urgency of initiating environmental conservation without delay.

To Reduce the Impact of Global Warming
Some of the repercussions stemming from global warming encompass shifts in the climate, the thawing of glaciers, the elevation of sea levels, the occurrence of acid rain, the greenhouse effect, and ocean acidification, among others. The underlying reasons behind the gradual elevation of our global temperature can be traced back to an expanding population and our negligent behaviors.
These concerns might not appear alarming until they begin to impact other facets of the environment. The heightened concentration of carbon in the atmosphere has brought about effects like climate shifts and the emergence of acid rain. The resultant acid, formed by the interaction of atmospheric carbon and rainwater, stands as a leading contributor to mortality rates in some of the most polluted nations. When this acid combines with ocean water, it elevates the pH level. Certain organisms are incapable of surviving beyond their optimal pH range, leading to a cascading effect through the entire food chain and ultimately causing ecosystem deterioration. Nevertheless, by fostering a comprehensive comprehension of the significance of environmental conservation, we hold the potential to shield our world from unforeseen natural disasters on the horizon.

To Bring Awareness
The final yet equally significant rationale for embarking on environmental conservation is to cultivate awareness within our populace. The existing array of environmental challenges we witness today can be attributed to our prolonged period of irresponsible conduct, pushing us toward an exceedingly catastrophic scenario that is hard to fathom. The initiation of all endeavors related to environmental preservation and conservation begins with an appreciation of its importance. This is because the outcomes bear the cumulative impact of our actions over time. Furthermore, by assuming the role of a responsible population and actively propagating awareness through participation in diverse environmental conservation initiatives, we can swiftly mitigate the subsequent consequences.

Conclusion
In conclusion, environmental conservation is not just a responsibility but a necessity for the well-being of our planet and future generations. By preserving natural ecosystems, reducing pollution, adopting sustainable practices, and promoting awareness, we can ensure the delicate balance of our environment. Each individual’s actions, no matter how small, contribute to the collective effort of safeguarding our planet’s beauty, resources, and diversity. Let us recognize that the Earth’s health is intricately linked to our own, and through thoughtful conservation, we can pave the way for a harmonious coexistence with nature.